Navigating the Financial Landscape: Understanding Nasdaq, Dow Jones, and Beyond
May 13, 2024 By Susan Kelly
What Are The Nasdaq And The Dow Jones
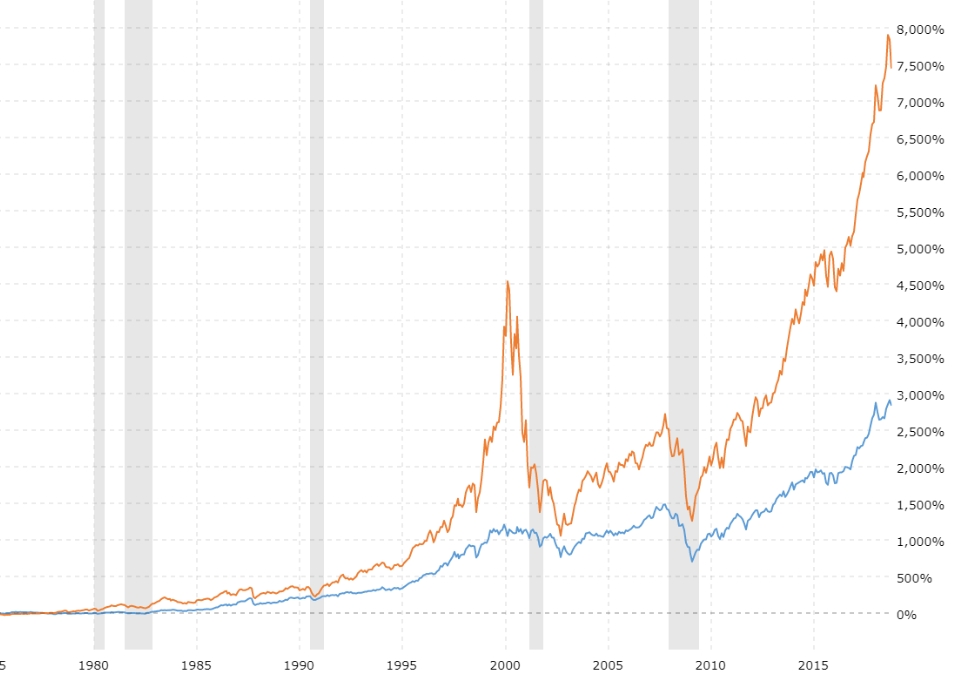 The Nasdaq and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) are two of the most prominent stock market indices globally, each with its own distinct characteristics, history, and significance in the financial world. Understanding these indices is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the stock market and make informed investment decisions.
The Nasdaq and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) are two of the most prominent stock market indices globally, each with its own distinct characteristics, history, and significance in the financial world. Understanding these indices is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the stock market and make informed investment decisions.
The Nasdaq, short for the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations, was established in 1971 as the world's first electronic stock market. Initially created to provide a transparent and efficient trading platform for over-the-counter (OTC) stocks, the Nasdaq has since evolved into a premier exchange, particularly renowned for its focus on technology and growth-oriented companies. The Nasdaq Composite Index, one of its key benchmarks, tracks the performance of more than 3,000 stocks listed on the exchange, spanning various sectors such as technology, biotechnology, telecommunications, and consumer discretionary. Notable constituents include tech giants like Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, and Alphabet (Google), among others. The Nasdaq's emphasis on innovation and growth makes it a preferred destination for investors seeking exposure to high-growth sectors and emerging trends.
In contrast, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, commonly referred to as the Dow, holds a rich historical legacy dating back to 1896 when it was first introduced by financial journalists Charles Dow and Edward Jones. Originally comprising just 12 industrial stocks, the Dow has expanded to include 30 large-cap, blue-chip companies representing a diverse array of sectors including technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods.
Key Differences Between Nasdaq And Dow Jones
 One of the most fundamental distinctions between the Nasdaq and the Dow lies in the weighting methodology employed by each index. The Nasdaq is market-capitalization-weighted, meaning that companies with higher market capitalizations exert a greater influence on the index's performance. This methodology reflects the Nasdaq's focus on growth-oriented companies, where larger firms typically command higher market valuations. In contrast, the Dow is price-weighted, with stocks' prices determining their influence on the index's movements. This unique approach gives greater weight to higher-priced stocks, regardless of their market capitalization, leading to a different distribution of influence among index constituents.
One of the most fundamental distinctions between the Nasdaq and the Dow lies in the weighting methodology employed by each index. The Nasdaq is market-capitalization-weighted, meaning that companies with higher market capitalizations exert a greater influence on the index's performance. This methodology reflects the Nasdaq's focus on growth-oriented companies, where larger firms typically command higher market valuations. In contrast, the Dow is price-weighted, with stocks' prices determining their influence on the index's movements. This unique approach gives greater weight to higher-priced stocks, regardless of their market capitalization, leading to a different distribution of influence among index constituents.
The sectors represented by the Nasdaq and the Dow also have implications for investor sentiment and market dynamics. The Nasdaq's heavy weighting towards technology and growth stocks makes it particularly sensitive to shifts in investor sentiment and market trends. During periods of optimism, the Nasdaq tends to outperform as investors flock to high-growth sectors, driving up stock prices. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of market volatility, the Nasdaq may experience sharper declines as investors rotate towards safer, defensive assets. In contrast, the Dow's broader representation of the economy gives it a more stable and less volatile profile, making it a preferred index for investors seeking relative safety and consistency.Moreover, the Nasdaq and the Dow offer investors different opportunities for diversification and risk management. Investing in the Nasdaq provides exposure to high-growth sectors and emerging trends, offering the potential for significant returns but also carrying higher levels of risk. In contrast, the Dow offers exposure to established, dividend-paying companies with proven track records of performance and stability, making it a preferred choice for investors seeking to mitigate risk and preserve capital.
How To Make Better Use Of Nasdaq And Dow Jones
One strategy for maximizing the utility of the Nasdaq and the Dow Jones involves incorporating thematic investing themes into portfolio construction. Thematic investing involves identifying and capitalizing on long-term trends and disruptive forces shaping the global economy. For instance, investors can utilize the Nasdaq's emphasis on technology and innovation to gain exposure to themes such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and renewable energy. By identifying companies driving these transformative trends and allocating capital accordingly, investors can position themselves to benefit from secular growth opportunities and outperform broader market indices.
Additionally, investors can harness the power of sector rotation strategies to optimize their utilization of the Nasdaq and the Dow Jones. Sector rotation involves reallocating capital across different sectors of the economy based on changing economic conditions, market trends, and cyclical factors. For example, during periods of economic expansion, investors may rotate towards sectors such as technology, consumer discretionary, and industrials, which are typically well-represented in the Nasdaq. Conversely, during economic downturns or periods of heightened uncertainty, investors may pivot towards defensive sectors such as healthcare, utilities, and consumer staples, which are more prevalent in the Dow Jones. By actively monitoring sectoral trends and adjusting their allocations accordingly, investors can enhance returns and manage risk more effectively.
Alternatives To The Nasdaq And The Dow Jones
One alternative to the Nasdaq and the Dow Jones is the S&P 500 Index, widely regarded as one of the most comprehensive benchmarks for the U.S. stock market. Comprising 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States, the S&P 500 offers broader exposure to the market than the Dow Jones, which consists of just 30 stocks. The S&P 500's market-capitalization-weighted methodology ensures that larger companies exert a greater influence on the index's performance, providing investors with a more representative snapshot of the U.S. equity market. Moreover, the S&P 500's diverse sectoral composition, spanning technology, healthcare, finance, consumer discretionary, and other sectors, makes it a preferred choice for investors seeking broad-based exposure to the U.S. economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Nasdaq and the Dow Jones Industrial Average undoubtedly hold significant sway in the financial world, representing distinct facets of the market and offering valuable insights for investors. However, as the investment landscape continues to evolve, it's essential for investors to recognize the limitations of relying solely on these traditional indices.

Susan Kelly Feb 24, 2024
Do You Know: What Is a Closing Statement?
79023

Triston Martin Oct 25, 2023
Conservative Investment Strategy
89810

Triston Martin May 13, 2024
Navigating Investment Choices: Robo Advisors vs. Financial Advisors
61083

Susan Kelly Jan 02, 2024
All About Combined Ratio
39177

Triston Martin May 13, 2024
Navigating the Twittersphere: A Comprehensive Guide to Buying Twitter Stock
63758

Triston Martin May 20, 2024
Deciphering Taxes on Your Social Security Income
70924

Susan Kelly Feb 20, 2024
A Guide to ACH: How Money Moves Around Without Checks
68083

Triston Martin May 21, 2024
Earn Cash for Your Shopping: 4 Apps That Pay You for Your Receipts
11173